为提升您基于新开发的Combo设备(同时支持Wi-Fi和BLE)硬件平台移植生活物联网平台SDK提供的蓝牙辅助Wi-Fi配网功能的效率,本文档将选择一款硬件开发板,进行实际的移植示例,将整个功能移植、应用开发、功能调试等过程串联起来供您参考。
Combo设备移植蓝牙辅助配网功能的主要流程如下。
选择硬件设备
设备研发生产厂商、模组厂商、芯片厂商等,根据您自己的产品与场景需要,选择合适的硬件平台(需有Combo芯片或模组)。
控制台创建产品
设备硬件选择好后,需在生活物联网平台控制台,创建项目和产品,新增测试设备,并配置好App的各项参数。
获取SDK
下载的生活物联网平台SDK中包含了所需的配网模块。
移植蓝牙辅助配网HAL
移植设备端生活物联网平台SDK(包括其中的Wi-Fi配网模块和蓝牙Breeze模块)到您的硬件平台上,并进行编译和调试。
生成设备固件
基于完整功能的示例应用,编译能运行于您硬件平台的蓝牙辅助配网设备固件。
验证蓝牙辅助配网功能
使用生活物联网平台提供的云智能App,验证蓝牙辅助配网功能。
一、准备硬件设备
请您根据自身产品选择合适的硬件设备,具体资源请参见蓝牙辅助配网开发(本文档以同时支持Wi-Fi和BLE的Combo芯片,BK7231U为示例)。
二、在控制台开发产品
三、获取SDK
获取生活物联网平台SDK时,建议您使用最新版本的含AliOS Things的SDK开发设备端。SDK下载地址请参见获取SDK。
四、移植蓝牙辅助配网HAL
蓝牙辅助配网同时使用了Wi-Fi和BLE的通信能力,因此该功能模块的移植,包括Wi-Fi配网模块和蓝牙Breeze模块的移植。
移植BLE协议栈。
蓝牙辅助配网中的BLE通信部分,使用了生活物联网平台的蓝牙Breeze(通过上层通信Profile的规则定义和实现)协议,基于蓝牙协议栈HAL的移植(需移植的HAL接口请参见蓝牙辅助配网开发)后,可以运行在不同厂商的蓝牙协议栈上。
以移植BK7231U型号的芯片为示例,在含AliOS Things的SDK代码包中,蓝牙Breeze模块及其需要移植的HAL位于/Living_SDK/framework/bluetooth/breeze/目录下,该目录中的内容说明如下。
内容
说明
breeze.mk
蓝牙Breeze模块的makefile
core/
蓝牙Breeze模块的协议实现,移植时不用了解其实现细节
include/
蓝牙Breeze模块的协议实现的头文件,移植时不用了解其实现细节
hal/
蓝牙Breeze模块的HAL实现,移植时需要重点实现,此处默认的实现是使用AliOS Things提供的开源BLE协议栈的移植实现
api/
供上层应用开发调用的用户编程接口,移植时可以不用了解其细节
该部分的移植,主要是实现breeze.mk(与编译控制相关)和HAL(与芯片蓝牙协议栈相关)的部分。
实现breeze.mk。
说明示例BK7231U基于GCC交叉编译工具链,采用
.mk的makefile的编译方式。如果您使用其他类型的编译工具,类似.mk的实现需完整移植到您所使用的编译工具环境下。NAME := breeze $(NAME)_MBINS_TYPE := kernel $(NAME)_VERSION := 1.0.0 $(NAME)_SUMMARY := breeze provides secure BLE connection to Alibaba IoT cloud and services. $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/core.c $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/transport.c $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/ble_service.c $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/sha256.c $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/utils.c GLOBAL_INCLUDES += api include hal/include $(NAME)_COMPONENTS := chip_code # Breeze安全广播功能,用于增强广播数据的安全性,蓝牙辅助配网中未使用 secure_adv ?= 0 ifeq ($(secure_adv), 1) GLOBAL_DEFINES += CONFIG_AIS_SECURE_ADV endif # 是否已移植并使用AliOS Things提供的开源BLE协议栈 # 如果厂商驱动中已包含自己的BLE协议栈,此项功能不用选择 # BK7231U使用的是厂商自己的BLE协议栈,因此这里不会使能 btstack ?= zephyr ifeq (zephyr, $(btstack)) $(NAME)_COMPONENTS += framework.bluetooth.breeze.hal.ble endif $(NAME)_SOURCES += api/breeze_export.c # Breeze安全认证功能,蓝牙辅助配网中必须打开 bz_en_auth ?= 1 ifeq ($(bz_en_auth), 1) GLOBAL_DEFINES += EN_AUTH $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/auth.c endif # Breeze辅助配网功能,蓝牙辅助配网中必须打开 bz_en_awss ?= 1 ifeq ($(bz_en_awss), 1) ifeq ($(bz_en_auth), 0) $(error awss need authentication, please set "bz_en_auth = 1") endif GLOBAL_DEFINES += EN_COMBO_NET GLOBAL_DEFINES += AWSS_REGION_ENABLE $(NAME)_SOURCES += core/extcmd.c $(NAME)_SOURCES += api/breeze_awss_export.c endif实现hal目录下的文件。
hal目录下面需要移植的文件分别是:breeze_hal_ble.h、breeze_hal_os.h、breeze_hal_sec.h。三个文件的实现请参见SDK代码包中/Living_SDK/platform/mcu/bk7231u/hal/breeze_hal/下的内容。
breeze_hal_ble.h
蓝牙协议栈移植接口,涉及BLE的广播、连接、GATT相关的内容,需实现breeze_hal_ble.c。
/** * API to initialize ble stack. * @parma[in] ais_init Bluetooth stack init parmaters. * @return 0 on success, error code if failure. */ // 对您使用的硬件平台的BLE协议栈初始化,协议栈初始化成功后,BLE功能才能正常使用 // 蓝牙辅助配网阶段,先初始化BLE协议栈,接着基于协议栈注册GATT Service,完成后才能通信 // Breeze的BLE通信通道是基于GATT Profile设计的,在设备端实现了Breeze的GATT Service // 生活物联网平台称之为AIS(Alibaba IoT Service) // 该GATT Service中是一组分别支持Read、Write、Notify、Indicate操作的Characteristic, // BLE协议栈初始化函数传入的是该GATT Primary Service的描述,BLE协议栈初始化函数需要将该Service // (也可以称为Attribute Table)注册到BLE stack,并将BLE链路的connect、disconnect与传入Service描述中的元素对应 // 通过该方式实现了BLE stack和AIS Service之间的联系, // 当BLE连接建立或断开,会通过初始化注册的connect、disconnect回调通知到Breeze模块中, // 同时在连接状态下对端对于AIS Service的操作,也会通过Read,Write等回调通知到Breeze模块中。 // 关于AIS Service的定义如下,供您移植和代码调试时参考 // Attribute Type |UUID |Properties |Permission // AIS Primary Service |0xFEB3 // Read Characteristic |0xFED4 |Read |Read // Write Characteristic |0xFED5 |Read/Write |Read/Write // Indicate Characteristic |0xFED6 |Read/Indicate |Indication // WriteWithNoRsp Characteristic |0xFED7 |Read/WriteCommand |Read/Write // Notify Characteristic |0xFED8 |Read/Notify |Notification ais_err_t ble_stack_init(ais_bt_init_t *ais_init); /** * API to de-initialize ble stack. * @return 0 on success, error code if failure. */ // 对您使用的硬件平台的BLE协议栈反初始化,如果在蓝牙辅助配网结束,设备将不会再使用BLE通信能力, // 对于此种BLE使用频率低的场景,可以在蓝牙通信功能完成后, // 将BLE协议栈反初始化,避免BLE协议栈持续开启但不使用,导致的不必要功耗和Wi-Fi、BLE共存问题 ais_err_t ble_stack_deinit(); /** * API to send data via AIS's Notify Characteristics. * @parma[in] p_data data buffer. * @parma[in] length data length. * @return 0 on success, error code if failure. */ // 通过前面注册的AIS Service的Notify Characteristic向连接链路的对端设备发送数据 ais_err_t ble_send_notification(uint8_t *p_data, uint16_t length); /** * API to send data via AIS's Indicate Characteristics. * @parma[in] p_data data buffer. * @parma[in] length data length. * @parma[in] txdone txdone callback. * @return 0 on success, erro code if failure. */ // 通过注册的AIS Service的Indicate Characteristic向连接链路的对端设备发送数据 ais_err_t ble_send_indication(uint8_t *p_data, uint16_t length, void (*txdone)(uint8_t res)); /** * API to disconnect BLE connection. * @param[in] reason the reason to disconnect the connection. */ // 从设备端主动断开已经建立的BLE连接 void ble_disconnect(uint8_t reason); /** * API to start bluetooth advertising. * @return 0 on success, erro code if failure. */ // 开始广播特定的内容,该内容为Manufacturer Specific Data,是Breeze填充, // 以便对端设备能够识别Breeze蓝牙设备所提供的服务,以及进行相关的身份校验 ais_err_t ble_advertising_start(ais_adv_init_t *adv); /** * API to stop bluetooth advertising. * @return 0 on success, erro code if failure. */ // 停止广播Breeze填充的特定的广播包,使支持Breeze协议的对端设备不要再发现此设备 ais_err_t ble_advertising_stop(); /** * API to start bluetooth advertising. * @parma[out] mac the uint8_t[BD_ADDR_LEN] space the save the mac address. * @return 0 on success, erro code if failure. */ // 获取设备的Bluetooth MAC地址,会用于身份识别等用途 ais_err_t ble_get_mac(uint8_t *mac);breeze_hal_os.h
OS系统移植接口,需实现breeze_hal_os.c。
/** * This function will create a timer. * * @param[in] timer pointer to the timer. * @param[in] fn callbak of the timer. * @param[in] arg the argument of the callback. * @param[in] ms ms of the normal timer triger. * @param[in] repeat repeat or not when the timer is created. * @param[in] auto_run run auto or not when the timer is created. * * @return 0: success. */ // 创建一个系统的software timer,参数可配置该timer的定时时长,定时触发的回调, // 是否反复定时,是否创建时立即运行timer等 // 下面几个接口是software timer操作相关,Breeze模块中会用来做定时触发和超时计算的用途, // 运行过程中可能会创建多个software timer int os_timer_new(os_timer_t *timer, os_timer_cb_t cb, void *arg, int ms); /** * This function will start a timer. * * @param[in] timer pointer to the timer. * * @return 0: success. */ // 运行前面创建好的software timer int os_timer_start(os_timer_t *timer); /** * This function will stop a timer. * * @param[in] timer pointer to the timer. * * @return 0: success. */ // 停止正在运行中的software timer,与前面的os_timer_start相对应 int os_timer_stop(os_timer_t *timer); /** * This function will delete a timer. * * @param[in] timer pointer to a timer. */ // 删除前面创建的一个系统的software timer,与os_timer_new相对应 void os_timer_free(os_timer_t *timer); /** * Reboot system. */ // 设备系统重启,一般在OTA一类的服务中,需要重启系统以便执行相关的固件搬移和系统初始化, // 类似这样的Breeze模块中的服务会需要用到该接口 void os_reboot(); /** * Msleep. * * @param[in] ms sleep time in milliseconds. */ // 系统睡眠和延时,有的操作需要等待某个动作发生才能执行下一步,就会用到该接口。 // 该接口在多线程实现中,一般会让所在线程休眠指定的时间,而不影响其他线程的执行 void os_msleep(int ms); /** * Get current time in mini seconds. * * @return elapsed time in mini seconds from system starting. */ // 获取系统的当前时间,该时间是一个相对系统启动点的相对时间,单位为ms long long os_now_ms(); /** * Add a new KV pair. * * @param[in] key the key of the KV pair. * @param[in] value the value of the KV pair. * @param[in] len the length of the value. * @param[in] sync save the KV pair to flash right now (should always be 1). * * @return 0 on success, negative error on failure. */ // 下面几个接口是Key-Value存储相关的接口,Breeze模块会用于一些数据的固化存储,目前蓝牙辅助配网 // 中暂时未固化存储数据,但考虑后续的功能扩展,Key-Value存储相关的接口也需要进行移植 // os_kv_set为将指定的数据存入Key-Value存储中 int os_kv_set(const char *key, const void *value, int len, int sync); /** * Get the KV pair's value stored in buffer by its key. * * @note: the buffer_len should be larger than the real length of the value, * otherwise buffer would be NULL. * * @param[in] key the key of the KV pair to get. * @param[out] buffer the memory to store the value. * @param[in-out] buffer_len in: the length of the input buffer. * out: the real length of the value. * * @return 0 on success, negative error on failure. */ // 从Key-Value存储中获取相应的数据 int os_kv_get(const char *key, void *buffer, int *buffer_len); /** * Delete the KV pair by its key. * * @param[in] key the key of the KV pair to delete. * * @return 0 on success, negative error on failure. */ // 将Key-Value存储中某个Key对应的数据删除 int os_kv_del(const char *key); /** * Generate random number. * * @return random value implemented by platform. */ // 返回一个随机值 int os_rand(void);breeze_hal_sec.h
安全算法移植接口,需实现breeze_hal_sec.c。
/** * @brief Initialize the aes context, which includes key/iv info. * The aes context is implementation specific. * * @param[in] key: * @param[in] iv: * @param[in] dir: AIS_AES_ENCRYPTION or AIS_AES_DECRYPTION * @return p_ais_aes128_t @verbatim None @endverbatim * @see None. * @note None. */ // 此部分为AES128算法的实现,Breeze模块通信是使用AES128 CBC加密的, // 因此务必保证该实现正常,否则会导致对端和设备间的通信异常 void *ais_aes128_init(const uint8_t *key, const uint8_t *iv); /** * @brief Destroy the aes context. * * @param[in] aes: the aex context. * @return @verbatim = 0: succeeded = -1: failed @endverbatim * @see None. * @note None. */ int ais_aes128_destroy(void *aes); /** * @brief Do aes-128 cbc encryption. * No padding is required inside the implementation. * * @param[in] aes: AES handler * @param[in] src: plain data * @param[in] block_num: plain data number of 16 bytes size * @param[out] dst: cipher data * @return @verbatim = 0: succeeded = -1: failed @endverbatim * @see None. * @note None. */ int ais_aes128_cbc_encrypt(void *aes, const void *src, size_t block_num, void *dst); /** * @brief Do aes-128 cbc decryption. * No padding is required inside the implementation. * * @param[in] aes: AES handler * @param[in] src: cipher data * @param[in] block_num: plain data number of 16 bytes size * @param[out] dst: plain data * @return @verbatim = 0: succeeded = -1: failed @endverbatim * @see None. * @note None. */ int ais_aes128_cbc_decrypt(void *aes, const void *src, size_t block_num, void *dst);
移植Wi-Fi协议栈。
蓝牙辅助配网中的BLE通信部分,使用了生活物联网平台的蓝牙Breeze协议,蓝牙Breeze属于上层通信Profile的规则定义和实现,基于蓝牙协议栈HAL的正确移植,可以运行于不同厂商的蓝牙协议栈之上。需移植的HAL接口(参见蓝牙辅助配网开发)。
以BK7231U的移植实现为示例,在含AliOS Things的生活物联网平台SDK的代码包中,Wi-Fi及其需要移植的HAL位于以下目录下。
/Living_SDK/framework/protocol/linkkit/sdk/iotx-sdk-c_clone/include/imports/
/Living_SDK/framework/protocol/linkkit/sdk/iotx-sdk-c_clone/include/iot_import.h
依赖的通用HAL的接口移植(如OS,LwIP,Security等)请参见Wi-Fi设备配网适配开发,对Wi-Fi HAL接口在BK7231U(基于AliOS Things)的移植实现示例说明如下。
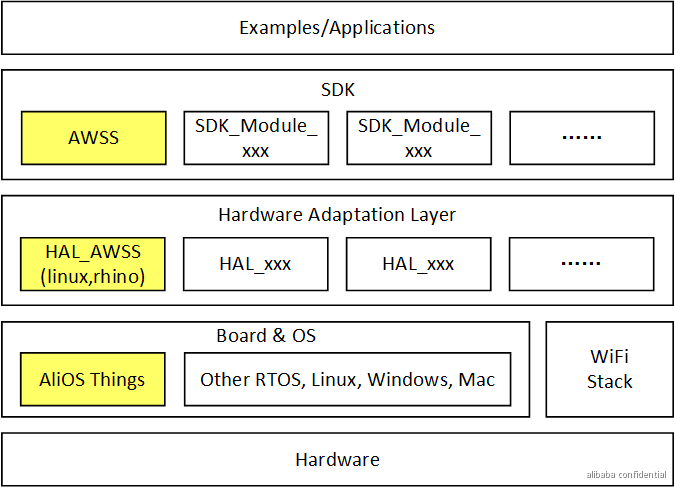
HAL_AWSS中的移植接口,有些是针对某种配网方式才需要实现的接口,对HAL_AWSS的所有HAL接口分类如下。
分类
说明
配网通用接口
所有配网方式都必须要实现的接口,包括蓝牙辅助配网、设备热点配网、一键配网、零配配网等
设备热点配网专用
需要支持设备热点配网方式时需实现的接口,如HAL_Awss_Open_Ap、HAL_Awss_Close_Ap等打开和关闭设备热点的接口
蓝牙辅助配网设备热点配网零配配网手机热点配网
需要支持这几种配网方式中的一种或几种时,需实现的接口HAL_Awss_Get_Conn_Encrypt_Type
一键配网专用
需要支持一键配网方式时需实现的接口,如HAL_Awss_Get_Encrypt_Type
编译相关控制。
编译配置文件请参见/Living_SDK/framework/protocol/linkkit/sdk/iotx-sdk-c_clone/make.settings。
# # Automatically generated file; DO NOT EDIT. # Main Menu # # # Configure Link Kit SDK for IoT Embedded Devices # FEATURE_SRCPATH="." FEATURE_MQTT_COMM_ENABLED=y FEATURE_ALCS_ENABLED=y # # MQTT Configurations # # FEATURE_MQTT_SHADOW is not set # FEATURE_MQTT_LOGPOST is not set FEATURE_MQTT_PREAUTH_SUPPORT_HTTPS_CDN=y FEATURE_DEVICE_MODEL_ENABLED=y FEATURE_MQTT_AUTO_SUBSCRIBE=y # # Device Model Configurations # # FEATURE_DEVICE_MODEL_GATEWAY is not set # 设备绑定的Feature需要打开,在设备配网完成后会和用户账户之间进行绑定 FEATURE_DEV_BIND_ENABLED=y # FEATURE_DEVICE_MODEL_RAWDATA_SOLO is not set # FEATURE_COAP_COMM_ENABLED is not set FEATURE_OTA_ENABLED=y # FEATURE_HTTP2_COMM_ENABLED is not set # FEATURE_HTTP_COMM_ENABLED is not set FEATURE_SUPPORT_TLS=y # FEATURE_SAL_ENABLED is not set # 设备Wi-Fi配网的Feature必须打开 FEATURE_WIFI_PROVISION_ENABLED=y # # AWSS Configurations # # 设备Wi-Fi配网可以支持的配网方式:一键配网、零配配网、设备热点配网(蓝牙辅助配网目前无需在此设置) FEATURE_AWSS_SUPPORT_SMARTCONFIG=y FEATURE_AWSS_SUPPORT_ZEROCONFIG=y FEATURE_AWSS_SUPPORT_DEV_AP=y实现配网通用接口。
/** * @brief 获取Wi-Fi设备的MAC地址, 格式应当是"XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX" * * @param mac_str : 用于存放MAC地址字符串的缓冲区数组 * @return 指向缓冲区数组起始位置的字符指针 */ char *HAL_Wifi_Get_Mac(_OU_ char mac_str[HAL_MAC_LEN]) { uint8_t mac[6] = { 0 }; // 调用驱动层的接口获取设备的MAC地址,并转为字符串的格式 hal_wifi_get_mac_addr(NULL, mac); snprintf(mac_str, HAL_MAC_LEN, "%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x", mac[0], mac[1], mac[2], mac[3], mac[4], mac[5]); return mac_str; } extern void wifi_get_ip(char ips[16]); /** * @brief 获取Wi-Fi网口的IP地址,点分十进制格式保存在字符串数组出参, * 二进制格式则作为返回值,并以网络字节序(大端)表达 * * @param ifname : 指定Wi-Fi网络接口的名字 * @param ip_str : 存放点分十进制格式的IP地址字符串的数组 * @return 二进制形式的IP地址,以网络字节序(大端)组织 */ uint32_t HAL_Wifi_Get_IP(_OU_ char ip_str[NETWORK_ADDR_LEN], _IN_ const char *ifname) { //(void *)ifname; // 调用驱动层的接口,获取设备的IP地址。该IP地址分为两种情况: // 1.一般情况,设备作为Station连接到AP,被分配的IP地址 // 2.设备支持设备热点,开启SoftAP模式时作为gateway的IP地址 wifi_get_ip(ip_str); return 0; } /** * @brief 获取在每个信道(`channel`)上扫描的时间长度,单位是毫秒 * 该接口主要是一键配网和零配配网会使用到,因为这两者在配网时 * 需要在Wi-Fi信道列表上进行轮询扫描 * * @return 时间长度, 单位是毫秒 * @note 推荐时长是200毫秒到400毫秒 */ int HAL_Awss_Get_Channelscan_Interval_Ms(void) { // 一般都设置为该默认的值 return 250; } /** * @brief 获取配网服务(`AWSS`)的超时时间长度,单位是毫秒 * * @return 超时时长,单位是毫秒 * @note 推荐时长是3分钟 */ int HAL_Awss_Get_Timeout_Interval_Ms(void) { // 一般都设置为该默认的值 return 3 * 60 * 1000; } /** * @brief 802.11帧的处理函数,可以将802.11 Frame传递给这个函数 * * @param[in] buf @n 80211 frame buffer, or pointer to struct ht40_ctrl * @param[in] len @n 80211 frame buffer length * @param[in] link_type @n AWSS_LINK_TYPE_NONE for most rtos HAL, * and for linux HAL, do the following step to check * which header type the driver supported. * @verbatim * a) iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor #open monitor mode * b) iwconfig wlan0 channel 6 #switch channel 6 * c) tcpdump -i wlan0 -s0 -w file.pacp #capture 80211 frame * & save d) open file.pacp with wireshark or omnipeek check the link header * type and fcs included or not * @endverbatim * @param[in] with_fcs @n 80211 frame buffer include fcs(4 byte) or not * @param[in] rssi @n rssi of packet */ awss_recv_80211_frame_cb_t g_ieee80211_handler; static void monitor_data_handler(uint8_t *buf, int len, hal_wifi_link_info_t *info) { int with_fcs = 0; int link_type = AWSS_LINK_TYPE_NONE; (*g_ieee80211_handler)((char *)buf, len, link_type, with_fcs, info->rssi); } /** * @brief 设置Wi-Fi网卡工作在监听(Monitor或Sniffer)模式, * 并在收到802.11帧的时候调用被传入的回调函数,回调函数的格式如上 * 必须要将802.11帧Buffer、长度、HAL类别,是否带有FCS、RSSI等信息提供给上层 * * @param[in] cb @n A function pointer, called back when wifi receive a * frame. */ void HAL_Awss_Open_Monitor(_IN_ awss_recv_80211_frame_cb_t cb) { // 这里BK7231U是移植了AliOS Things的驱动移植层的,因此是hal_wifi_module // 风格的实现。这里主要是将回调先注册到驱动层,并开启Monitor模式, // 在监听到802.11的帧时,都通过回调函数上报上去 hal_wifi_module_t *module = hal_wifi_get_default_module(); if (module == NULL) { return; } g_ieee80211_handler = cb; hal_wifi_register_monitor_cb(module, monitor_data_handler); hal_wifi_start_wifi_monitor(module); HAL_Awss_Switch_Channel(6, 0, NULL); } /** * @brief 设置Wi-Fi网卡离开监听(Monitor或Sniffer)模式, * 并开始以站点(Station)模式工作 */ void HAL_Awss_Close_Monitor(void) { // 将原来注册的回调函数取消(设置为NULL),并关闭设备的Monitor模式, hal_wifi_module_t *module; module = hal_wifi_get_default_module(); if (module == NULL) { return; } hal_wifi_register_monitor_cb(module, NULL); hal_wifi_stop_wifi_monitor(module); } /** * @brief handle one piece of AP information from Wi-Fi scan result * * @param[in] ssid @n name of AP * @param[in] bssid @n mac address of AP * @param[in] channel @n AP channel * @param[in] rssi @n rssi range[-127, -1]. * the higher the RSSI number, the stronger the signal. * @param[in] is_last_ap @n this AP information is the last one if * is_last_ap > 0. this AP information is not the last one if is_last_ap == * 0. * @return 0 for Wi-Fi scan is done, otherwise return -1 * @see None. * @note None. */ typedef int (*awss_wifi_scan_result_cb_t)(const char ssid[HAL_MAX_SSID_LEN], const uint8_t bssid[ETH_ALEN], enum AWSS_AUTH_TYPE auth, enum AWSS_ENC_TYPE encry, uint8_t channel, signed char rssi, int is_last_ap); /** * @brief 启动一次Wi-Fi的空中扫描(Scan) * 该模式需要与前面的Monitor(或Sniffer)模式区别, * Monitor(Sniffer):持续开启802.11帧监听,并实时上报监听到的帧,直到该模式被关闭 * Scan:扫描AP(通过Beacon和Probe Request帧),并记录一次扫描到的多个AP的结果 * * @param[in] cb @n pass ssid info(scan result) to this callback one by one * @return 0 for Wi-Fi scan is done, otherwise return -1 * @see None. * @note * This API should NOT exit before the invoking for cb is finished. * This rule is something like the following : * HAL_Wifi_Scan() is invoked... * ... * for (ap = first_ap; ap <= last_ap; ap = next_ap){ * cb(ap) * } * ... * HAL_Wifi_Scan() exit... */ int HAL_Wifi_Scan(awss_wifi_scan_result_cb_t cb) { // 注册Scan到的AP列表的回调函数 // 并启动Scan(对周边AP的扫描,建议实现为active scan,扫到的效率更高) // 该函数是同步执行的方式,即调用后线程会被其阻塞,直到本次扫描结束 netmgr_register_wifi_scan_result_callback( (netmgr_wifi_scan_result_cb_t)cb); hal_wifi_start_scan_adv(NULL); while (netmgr_get_scan_cb_finished() != true) { // block aos_msleep(50); } return 0; } /** * @brief 设置Wi-Fi网卡切换到指定的信道(channel)上 * * @param[in] primary_channel @n Primary channel. * @param[in] secondary_channel @n Auxiliary channel if 40Mhz channel is * supported, currently this param is always 0. * @param[in] bssid @n A pointer to Wi-Fi BSSID on which awss lock the * channel, most HAL may ignore it. */ void HAL_Awss_Switch_Channel(_IN_ char primary_channel, _IN_OPT_ char secondary_channel, _IN_OPT_ uint8_t bssid[ETH_ALEN]) { hal_wifi_module_t *module; module = hal_wifi_get_default_module(); if (module == NULL) { return; } // 调用驱动层接口,设置设备此时工作在指定的信道,对于某些应用需要,指定信道 // 会使一些操作更加高效 hal_wifi_set_channel(module, (int)primary_channel); } /** * @brief 要求Wi-Fi网卡连接指定热点(Access Point)的函数 * * @param[in] connection_timeout_ms @n AP connection timeout in ms or HAL_WAIT_INFINITE * @param[in] ssid @n AP ssid * @param[in] passwd @n AP passwd * @param[in] auth @n optional(AWSS_AUTH_TYPE_INVALID), AP auth info * @param[in] encry @n optional(AWSS_ENC_TYPE_INVALID), AP encry info * @param[in] bssid @n optional(NULL or zero mac address), AP bssid info * @param[in] channel @n optional, AP channel info * @return @verbatim = 0: connect AP & DHCP success = -1: connect AP or DHCP fail/timeout @endverbatim * @see None. * @note * If the STA connects the old AP, HAL should disconnect from the old AP firstly. */ int HAL_Awss_Connect_Ap(_IN_ uint32_t connection_timeout_ms, _IN_ char ssid[HAL_MAX_SSID_LEN], _IN_ char passwd[HAL_MAX_PASSWD_LEN], _IN_OPT_ enum AWSS_AUTH_TYPE auth, _IN_OPT_ enum AWSS_ENC_TYPE encry, _IN_OPT_ uint8_t bssid[ETH_ALEN], _IN_OPT_ uint8_t channel) { int ms_cnt = 0; netmgr_ap_config_t config = { 0 }; if (ssid != NULL) { strncpy(config.ssid, ssid, sizeof(config.ssid) - 1); } if (passwd != NULL) { strncpy(config.pwd, passwd, sizeof(config.pwd) - 1); } if (bssid != NULL) { memcpy(config.bssid, bssid, ETH_ALEN); } // 将要连接的AP的信息暂存下来 netmgr_set_ap_config(&config); // 在正式连接AP前,Suspend Station,防止设备受上一次操作未结束的干扰 hal_wifi_suspend_station(NULL); // LOGI("aos_awss", "Will reconnect wifi: %s %s", ssid, passwd); // 实际会调用驱动层接口,向指定的AP发起连接 netmgr_reconnect_wifi(); // 在调用驱动层接口去连接AP后,在此阻塞线程一断时间,该段时间内持续检查设备当前是否 // 已经连接AP成功且获取到了IP地址,如果获取到IP地址,该函数结束,并返回连接成功的结果 while (ms_cnt < connection_timeout_ms) { if (netmgr_get_ip_state() == false) { LOGD("[waitConnAP]", "waiting for connecting AP"); aos_msleep(500); ms_cnt += 500; } else { LOGI("[waitConnAP]", "AP connected"); return 0; } } // if AP connect fail, should inform the module to suspend station // to avoid module always reconnect and block Upper Layer running // 如果在连接AP超时时间到达,都没能成功连上AP,或者连上了AP没能获取到IP地址,说明设备 // 本次发起连接是失败的(可能是AP的ssid,密码等信息有误,或者是AP本身工作异常,或者是 // 干扰太强或信号太弱导致没法顺利连接上),那么此时Suspend Station(驱动层可能还在 // 处于对AP发起连接的状态,Suspend Station将该状态终止,使设备不再向AP发起连接), // 最后返回连接失败的结果给上层处理 hal_wifi_suspend_station(NULL); return -1; } #define FRAME_ACTION_MASK (1 << FRAME_ACTION) #define FRAME_BEACON_MASK (1 << FRAME_BEACON) #define FRAME_PROBE_REQ_MASK (1 << FRAME_PROBE_REQ) #define FRAME_PROBE_RESP_MASK (1 << FRAME_PROBE_RESPONSE) #define FRAME_DATA_MASK (1 << FRAME_DATA) /** * @brief 在当前信道(channel)上以基本数据速率(1Mbps)发送裸的802.11帧(raw * 802.11 frame) * * @param[in] type @n see enum HAL_Awss_frame_type, currently only * FRAME_BEACON,FRAME_PROBE_REQ is used * @param[in] buffer @n 80211 raw frame, include complete mac header & FCS field * @param[in] len @n 80211 raw frame length * @return @verbatim = 0, send success. = -1, send failure. = -2, unsupported. @endverbatim * @see None. * @note awss use this API send raw frame in Wi-Fi monitor mode & station mode */ int HAL_Wifi_Send_80211_Raw_Frame(_IN_ enum HAL_Awss_Frame_Type type, _IN_ uint8_t *buffer, _IN_ int len) { // 调用驱动层的接口发送802.11的帧,类型必须要支持上面定义的5种 return hal_wlan_send_80211_raw_frame(NULL, buffer, len); } /** * @brief 管理帧的处理回调函数 * * @param[in] buffer @n 80211 raw frame or ie(information element) buffer * @param[in] len @n buffer length * @param[in] rssi_dbm @n rssi in dbm * @param[in] buffer_type @n 0 when buffer is a 80211 frame, * 1 when buffer only contain IE info * @return None. * @see None. * @note None. */ typedef void (*awss_wifi_mgmt_frame_cb_t)(_IN_ uint8_t *buffer, _IN_ int len, _IN_ signed char rssi_dbm, _IN_ int buffer_type); static awss_wifi_mgmt_frame_cb_t monitor_cb = NULL; static void mgnt_rx_cb(uint8_t *data, int len, hal_wifi_link_info_t *info) { if (monitor_cb) { monitor_cb(data, len, info->rssi, 0); } } /** * @brief 使能或禁用对管理帧的过滤 * * @param[in] filter_mask @n see mask macro in enum HAL_Awss_frame_type, * currently only FRAME_PROBE_REQ_MASK & FRAME_BEACON_MASK is used * @param[in] vendor_oui @n oui can be used for precise frame match, optional * @param[in] callback @n see awss_wifi_mgmt_frame_cb_t, passing 80211 * frame or ie to callback. when callback is NULL * disable sniffer feature, otherwise enable it. * @return @verbatim = 0, success = -1, fail = -2, unsupported. @endverbatim * @see None. * @note awss use this API to filter specific mgnt frame in Wi-Fi station mode */ int HAL_Wifi_Enable_Mgmt_Frame_Filter( _IN_ uint32_t filter_mask, _IN_OPT_ uint8_t vendor_oui[3], _IN_ awss_wifi_mgmt_frame_cb_t callback) { monitor_cb = callback; // 管理帧的过滤开启与关闭,都在此接口中实现,开启时需传入有效的回调函数,而传入NULL时 // 表示将管理帧的过滤功能关闭。 // 管理帧过滤的开启时机,可能在设备处于Station模式,也可能在设备处于设备热点模式, // 因此只要设备Wi-Fi stack能获取到周边的管理帧,都需要能支持管理帧的过滤开启 if (callback != NULL) { hal_wlan_register_mgnt_monitor_cb(NULL, mgnt_rx_cb); } else { hal_wlan_register_mgnt_monitor_cb(NULL, NULL); } return 0; } /** * @brief check system network is ready(get ip address) or not. * * @param None. * @return 0, net is not ready; 1, net is ready. * @see None. * @note None. */ int HAL_Sys_Net_Is_Ready() { // 调用接口判断设备当前的IP地址是否有效 return netmgr_get_ip_state() == true ? 1 : 0; } /** * @brief 获取所连接的热点(Access Point)的信息 * * @param[out] ssid: array to store ap ssid. It will be null if ssid is not required. * @param[out] passwd: array to store ap password. It will be null if ap password is not required. * @param[out] bssid: array to store ap bssid. It will be null if bssid is not required. * @return @verbatim = 0: succeeded = -1: failed @endverbatim * @see None. * @note None. */ int HAL_Wifi_Get_Ap_Info(_OU_ char ssid[HAL_MAX_SSID_LEN], _OU_ char passwd[HAL_MAX_PASSWD_LEN], _OU_ uint8_t bssid[ETH_ALEN]) { netmgr_ap_config_t config = { 0 }; netmgr_get_ap_config(&config); if (ssid) { strncpy(ssid, config.ssid, HAL_MAX_SSID_LEN - 1); } if (passwd) { #ifdef DISABLE_SECURE_STORAGE strncpy(passwd, config.pwd, HAL_MAX_PASSWD_LEN - 1); #else extern int iotx_ss_decrypt(const char* in_data, int in_len, char* out_data, int out_len); iotx_ss_decrypt(config.pwd, MAX_PWD_SIZE, passwd, MAX_PWD_SIZE); #endif } if (bssid) { memcpy(bssid, config.bssid, ETH_ALEN); } return 0; } /** * @brief 获取当前Station模式与AP连接状态的信息 * * @param[out] p_rssi: rssi value of current link * @param[out] p_channel: channel of current link * * @return @verbatim = 0: succeeded = -1: failed @endverbatim * @see None. * @note None. * @note awss use this API to get rssi and channel of current link */ int HAL_Wifi_Get_Link_Stat(_OU_ int *p_rssi, _OU_ int *p_channel) { int ret; hal_wifi_link_stat_t link_stat; if (netmgr_get_ip_state() == true) { ret = hal_wifi_get_link_stat(NULL, &link_stat); if ((ret == 0) && link_stat.is_connected) { *p_rssi = link_stat.wifi_strength; *p_channel = link_stat.channel; } else { return -1; } } else { return -1; } return 0; }实现蓝牙辅助配网关联的专用接口。
/** * @brief Get Security level for Wi-Fi configuration with connection. * Used for AP solution of router and App. * * @param None. * @return The security level: @verbatim 3: aes128cfb with aes-key per product and aes-iv = random 4: aes128cfb with aes-key per device and aes-iv = random 5: aes128cfb with aes-key per manufacture and aes-iv = random others: invalid @endverbatim * @see None. */ int HAL_Awss_Get_Conn_Encrypt_Type() { char invalid_ds[DEVICE_SECRET_LEN + 1] = {0}; char ds[DEVICE_SECRET_LEN + 1] = {0}; // 用于区分该种配网方式的加密方式是使用“一机一密”还是“一型一密” // 如果DeviceSecret可以获取到,则使用“一机一密”的高安全级别加密方式 // 如果设备本地未找到DeviceSecret,则降级使用“一型一密”的次高安全级别加密方式 HAL_GetDeviceSecret(ds); if (memcmp(invalid_ds, ds, sizeof(ds)) == 0) return 3; memset(invalid_ds, 0xff, sizeof(invalid_ds)); if (memcmp(invalid_ds, ds, sizeof(ds)) == 0) return 3; return 4; }
五、生成设备固件
生活物联网平台SDK提供了蓝牙辅助配网的示例应用,完成移植后,可以基于示例应用编译蓝牙辅助配网设备固件,并对蓝牙辅助配网的整体功能进行快速验证。
SDK版本 | 编译指令 |
1.3.0以上版本 | ./build.sh example smart_outlet bk7231udevkitc MAINLAND ONLINE 1 |
1.3.0及以下的版本 | cd Living_SDK aos make clean aos make comboapp@bk7231udevkitc btstack=vendor |
初始化与启动应用。
int application_start(int argc, char **argv)示例应用目录中的app_entry.c文件的
application_start函数,该函数主要实现如下功能。系统初始化与启动
设备调试日志等级、设备信息、设备诊断模块设置
Wi-Fi模块初始化,以及相关的事件订阅
串口交互命令
cli的初始化和注册Wi-Fi模块的启动,与相关任务的创建
动态开启或关闭设备的蓝牙辅助配网模式。
实现设备系统与各模块的初始化后,通过如下代码实现,可以动态开启或关闭设备的蓝牙辅助配网模式。
// 关闭蓝牙辅助配网功能 breeze_awss_stop(); // 开启蓝牙辅助配网功能 breeze_awss_start();实现蓝牙辅助配网工作流程。
示例应用的其核心流程实现在示例应用目录中的combo_net.c文件的
combo_net_init函数。该函数主要实现以下功能。注册应用层的回调,会触发去连接路由器。
将设备信息设置到下层的Breeze SDK中。
初始化并开启蓝牙辅助配网的BLE通信通道。
设备发出BLE广播(广播里面会携带蓝牙辅助配网功能的标识),处于BLE广播状态的设备可以被移动端App扫描发现。此时App上的操作过程以及设备的状态变化说明如下。
设备进入蓝牙辅助配网状态时,开始持续发出BLE广播,广播里携带蓝牙辅助配网功能的标识。
移动端App扫描发现该待配网的Combo设备,并从移动端App发起与该设备建立连接的请求。
建立连接时,移动端App与设备之间通过安全认证,确保建立的BLE连接是安全可靠的。
App通过BLE安全连接通道下发配网信息给设备端。
设备端通过Breeze SDK,接收和解析配网信息。
设备端在获取到配网信息后,触发注册的
combo_service_event事件处理函数(此时底层SDK已经获取到了Wi-Fi联网需要的路由器的SSID和密码等信息)。combo_service_event事件处理函数时,会检测路由器的SSID和信号强度等情况,并向路由器发起连接请求。连接路由器成功后,获取IP地址,启动设备连云。
说明整个过程中如果出现异常,设备端会通过异常自检生成关键错误码信息,通过和移动端App之间的BLE连接传回,并在移动端App界面显示。
int combo_net_init() { breeze_dev_info_t dinfo = { 0 }; // 注册获取到App端传过来的配网信息时的回调,会触发去连接路由器的动作 aos_register_event_filter(EV_BZ_COMBO, combo_service_event, NULL); if ((strlen(g_combo_pk) > 0) && (strlen(g_combo_ps) > 0) \ && (strlen(g_combo_dn) > 0) && (strlen(g_combo_ds) > 0) && g_combo_pid > 0) { // 设备信息设置到下层的SDK中,蓝牙辅助配网与一般的Wi-Fi设备相比, // 会多一个PID的设备信息,专用于蓝牙的通信握手等功能之用 dinfo.product_id = g_combo_pid; dinfo.product_key = g_combo_pk; dinfo.product_secret = g_combo_ps; dinfo.device_name = g_combo_dn; dinfo.device_secret = g_combo_ds; // 初始化蓝牙辅助配网所需的BLE协议栈、Breeze SDK等,并注册获取到配网信息的回调 // 同时正式启动蓝牙辅助配网 breeze_awss_init(apinfo_ready_handler, &dinfo); breeze_awss_start(); } else { // 如果设备信息设置有误,则无法进行蓝牙辅助配网 printf("combo device info not set!\n"); } return 0; }调试蓝牙辅助配网设备。
编译生成设备固件,并烧录到相应的开发板之后,可以通过如下的串口命令,触发设备的相应动作(生活物联网平台SDK 1.3.0及之后的版本才支持动态串口命令交互)。
烧录设备证书信息。
蓝牙相关的设备证书包括ProductKey、DeviceName、DeviceSecret、ProductSecret、ProductID(您在生活物联网控制台创建的产品与设备后平台自动颁发的),在设备上电初始执行以下命令烧录设备证书信息。
linkkey ProductKey DeviceName DeviceSecret ProductSecret ProductID开启一键配网功能。
此时如果蓝牙辅助配网进行中,会先自动关闭蓝牙辅助配网功能。
awss active_awss开启蓝牙辅助配网功能。
在设备正常启动后,默认会进入信道扫描的状态。此时如果一键配网进行中,会先自动关闭一键配网功能。
ble_awss启动蓝牙辅助配网后,设备会通过BLE广播自己的蓝牙辅助配网相关的设备信息,移动端的App可在其设备发现页面发现处于待配网状态的设备。通过在移动端App界面可发起对设备的蓝牙辅助配网,配网过程、配网结果、配网过程中发生的异常等信息会通过移动端App界面实时展示。
清除设备配网信息。
reset
六、验证蓝牙辅助配网功能
您可以使用生活物联网平台提供的云智能App(公版App)来验证蓝牙辅助配网功能。
下载云智能App(2.7.5或以上的版本)。下载方式请参见云智能App介绍。
登录云智能App。
打开手机系统的蓝牙开关。
进入App的设备发现界面,开始扫描发现蓝牙辅助配网状态的设备。
如果设备无法发现,请检查确保以下各项是否设置有误。
设备是否已处于蓝牙广播状态(可使用相关工具搜索,如nRF Connect App)。
蓝牙辅助配网广播内容示例说明如下。
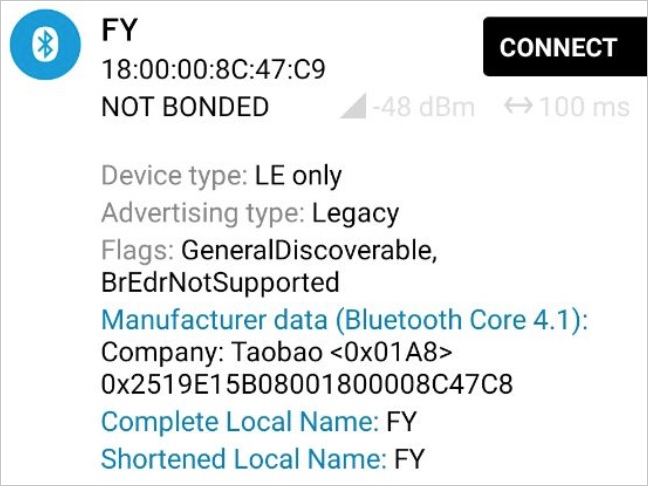
广播数据内容主要位于广播的Manufacturer data字段中,其中包含Company ID和一些服务支持标识,以及MAC地址。其中MAC地址是表示Wi-Fi MAC(Combo实际上是Wi-Fi设备,此处蓝牙只是作为辅助配网,设备和云端通信链路通过Wi-Fi),此处Wi-Fi MAC地址为
C8:47:8C:00:00:18。设备证书信息是否设置正确(使用linkkey命令设置的内容)。
App的账号环境与创建设备产品的站点是否对应。
控制台人机交互中是否配置了蓝牙辅助配网的配网方式。
App界面发现蓝牙辅助配网设备后,点击即可开始蓝牙辅助配网流程,其间需要输入手机连着的路由器的SSID和密码,并且在App UI界面确认设备已处于配网状态,用户界面确认完毕后,App端会去和设备建立蓝牙连接。
如果蓝牙连接在短时间内断开,请检查确保以下项是否正常。
设备证书信息是否设置正确(使用linkkey命令设置的内容)。
设备BLE协议栈移植以及示例应用的实现是否检查确认无误
手机连着的路由器的网络是否能正常使用
手机将路由器信息传输给设备端,设备收到信息后去连接目标路由器。
此时设备与手机之间的蓝牙连接不会断开,设备连接路由器、连接云端过程中如果有失败情况发生,设备会启动自检(需升级至生活物联网平台SDK 1.3.0之后的版本才支持失败详情自检的能力),并将自检结果通过蓝牙连接返回给手机,并在App界面上显示。
App界面跳转出设备的控制界面(如“灯”产品的控制界面可以开关灯,调整灯的亮度等)。
此时,蓝牙辅助配网的功能调试成功。接下来您需要对设备产品的完整功能、稳定性能、成功率等进行严格测试把控,最终完成整个方案的量产和发布。